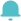
Surge protection connection (not only) to the switchboard
Surge protection connection – CT1 connection type
This connection provides a mode of protection between each active (L/N) conductor and PE (PEN) which is ideal for eliminating the lightning surge (common-mode) as it provides a shorter way of balancing the potential and thus a smaller voltage protection level between the active conductors and PE respectively PEN (only one protective element). All protective elements used in this connection are identical. The disadvantage of the CT1 connection is that the N and PE conductors are not galvanically separated. If an SPD is installed behind a RCD (Residual Current Device), the risk of its unwanted activation increases. This can be caused by permanent leakage currents using varistor elements only or by small surges where the current flows through the SPD connected between the L and PE conductors - the RCD can evaluate it as an error current and cause an unwanted circuit shutdown. Due to the protection principle and disadvantage mentioned above the CT1 connection is used mostly for SPDs type T1 or SPDs type T1+T2, that are connected at the beginning of the installation in the main switchboards where the current protectors are not yet installed and where the common-mode surge occurs the most. The standard HD 60364-5-53:2022 makes CT1 connection mandatory.
| Configuration | Power supply system | Number of phases | Number of protective elements | Protective element between conductors |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1+0 | TN-C, TN-C-S * | 1 | 1 | L-PEN |
| 2+0 | TN-C-S, TN-S | 1 | 2 | L-PE, N-PE |
| 3+0 | TN-C, TN-C-S * | 3 | 3 | L1-PEN, L2-PEN, L3-PEN |
| 4+0 | TN-C-S, TN-S | 3 | 4 | L1-PE, L2-PE, L3-PE, N-PE |
Tab. Surge protection configuration in connection type CT1
* The possibility to use the configuration 1+0 or 3+0 in TN-C-S systems is given by the condition of the
cable length between the SPD PEN terminal and the point of splitting of the PEN conductor into N and PE,
which is set at less than 0.5 m (in cases where the SPD and the point of splitting are located in one
switchboard)
Fig. 1 Surge protection wiring diagram – CT1 type connection in configuration 3+0
Fig. 2 Surge protection wiring diagram – CT1 type connection in configuration 4+0
-
T1T2LIGHTNING AND SURGE ARRESTERS T1+T2:
Surge protection connection – CT2 type connection
This provides a mode of protection between each phase conductor and the neutral conductor N and between the neutral conductor N and PE, which is ideal for switching and industrial surge (differential mode) as it provides a shorter path of potential equalization and thus a smaller voltage protective level between the phase conductors and the neutral conductor N (only one protective element). Due to the protection principle the CT2 connection is mainly used for SPDs type T2 and T3 - these are connected further in the installation, for example in secondary switchboards, or close to the equipment to be protected. All protective elements between active conductors are identical so a sum element is inserted between N and PE– most often a GDT (Gas Discharge Tube). The sum element means that the discharge capability of such element must be at least the sum of the discharge capabilities of all protective elements between active conductors. The advantage of this connection type is the galvanic separation of the N conductor and the PE protective conductor. If an SPD is installed behind a RCD (Residual Current Device), the risk of unwanted activation does not increase. Neither because of leakage currents into the PE conductor using varistor elements nor because of small surges when the sum element (GDT) remains in a state of high impedance and the current flows only through the surge protection connected between conductors L1, L2, L3 and N. The RCD does not react to such current and does not cause an unwanted circuit shutdown.
| Configuration | Power supply system | Number of phases | Number of protective elements | Protective element between conductors |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1+1 | TN-S, TN-C-S | 1 | 2 | L-N, N-PE |
| 3+1 | TN-S, TN-C-S | 3 | 4 | L1-N, L2-N, L3-N, N-PE |
Tab. Surge protection configuration in CT2 type connection
Fig. 3 Surge protection wiring diagram - CT2 type connection in 3+1 configuration
-
T2T3Surge arresters T2+T3: